Google’s Accelerated Mobile Page (AMP) is the Internet giant’s answer to Facebook’s Instant Articles, and to Apple’s Apple News. Apple and Facebook are able to provide fast-loading content on their closed platforms.
Google joined the move to provide mobile users with content that load faster through its Google AMP project. Unlike Apple News and Instant Articles, Google AMP is open-source. That means that everyone will be able to provide a better surfing experience for mobile users as they transition to AMP.
Google stresses that a big chunk of the reasons why ordinary websites load slow are because of how things are placed on web pages. The problem areas include having multiple JavaScript libraries, coupled document and resource layouts, CSS and extensions that block rendering, style recalculations, and others.
An In-depth look on Google AMP’s mechanism
A lot of technicalities are involved on how Google was able to resolve the problem areas, ending up with fast-rendering web pages. The following is a technical discussion on how Google AMP makes web pages load faster than ever:
First, Google AMP makes use of AMP HTML, a restricted subset of HTML. AMP HTML corrects the problem areas that make rendering slow, significantly improving web performance.
Google AMP also makes use of AMP Runtime, a custom Javascript app. It controls the AMP pages’ rendering, and binds all resources to strict specifications.
AMP HTML and AMP runtime restricts content through the following ways:
- Custom JavaScript is not allowed except on certain pre-approved components. There are no libraries, and no frameworks.Even jQuery snippets are not allowed.
- iFrames are not allowed.
- Form elements, except for buttons, are not allowed.
- Tags for images, videos, and audio are replaced by AMP versions. These are controlled by AMP runtime.
- CSS must have only a single
Although there are lots of restrictions for Google AMP, it is at least available for other websites (contrary to what Facebook and Apple did for Instant Articles and Apple News). You will be able to AMP up your website, making it load faster, for a richer mobile surfing experience.
But how really does Google AMP make loading faster?
Google AMP really put web performance on its focus. The AMP HTML was built to really hasten rendering of pages.
Here is how the aforementioned technicalities make page rendering faster:
- There is only a small number of initial server request.
- JavaScript and other media are lazy-loaded.
- Risk for out-of-control author-written JavaScript is eliminated.
- Priority is given to above-the-fold content.
- Dimensions of resources are known by default so there is no need for recalculation.
Supported CSS styles in AMP
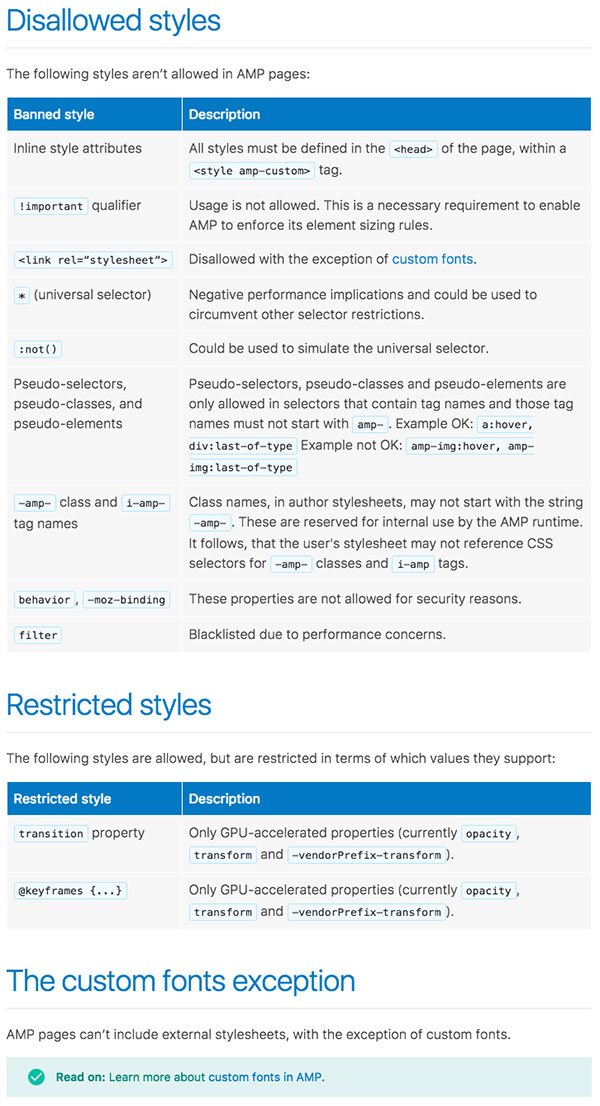
Learn more about custom fonts in AMP. To learn more about supported CSS in AMP, go to ampproject.org.
Fret not, Custom Components are available!
You might be worried that maybe the real reason why Google AMP is able to offer fast-rendering pages is because that will leave you with basic HTML and CSS only. Don’t worry because you will have widgets at your disposal, only that these are pre-approved.
Currently, there are 12 approved components which include amp-img, amp-ad, and amp-video, amp-anim, amp-pixel, and amp-twitter. Image carousels, maps, social plug-ins, and data visualization are expected to be supported sooner or later.
For now, it can be presumed that any component can be added to the list of approved components for as long as the minds behind the Google AMP project will be able to optimize them.
Google AMP is still on its early ages and we can expect a lot more from it as it develops further. A truly faster and richer mobile surfing experience await for us all! Let us all look forward for the development of Google AMP.